RD
How does the on-board drone radar work?
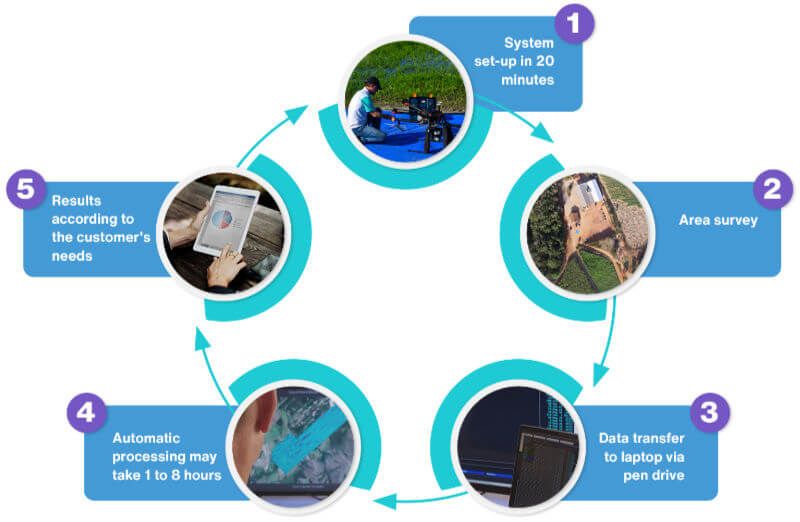
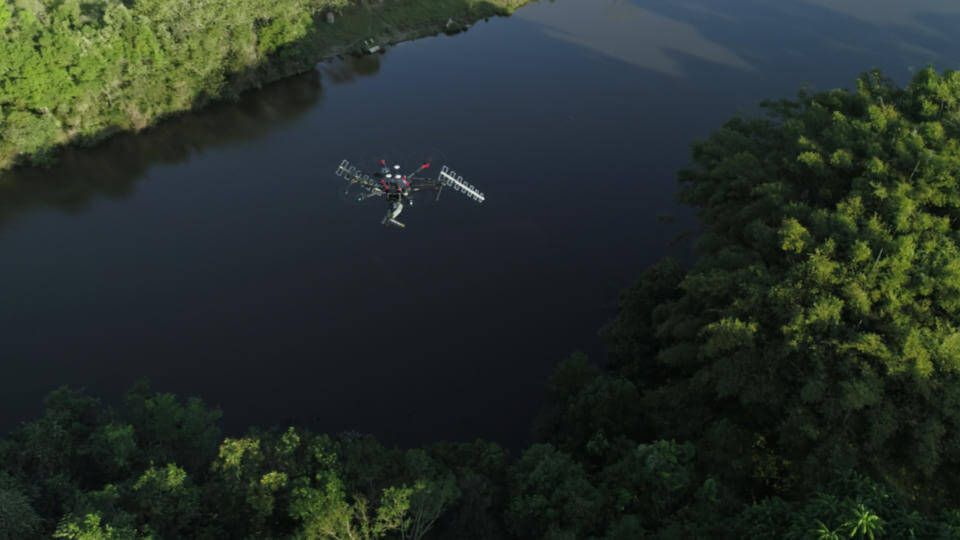
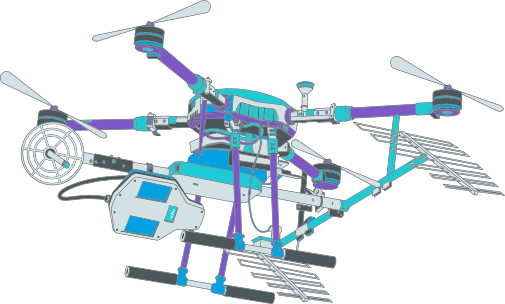
The radar together with the C, L and P antennas is installed on a class 3 drone (1). The equipment then flies over the desired area and can cover up to 500 hectares per day in linear mode and up to 50 hectares per day in helical mode (2). After the flight the data on the USB sticks is collected from the GNSS ground station and radar on the drone and passed to the laptop where it will be processed (3).
The processing can take from 1 - 8 hours depending on the application and flight time (4). Once completed, a report is generated with images and information of the overflown area, which can be viewed on the client's laptop or tablet (5).
What do antennas do?
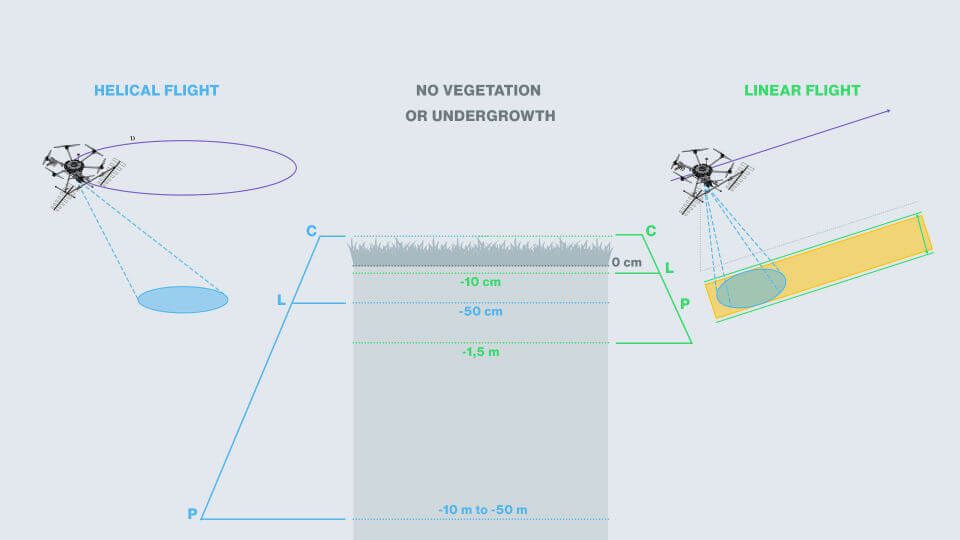
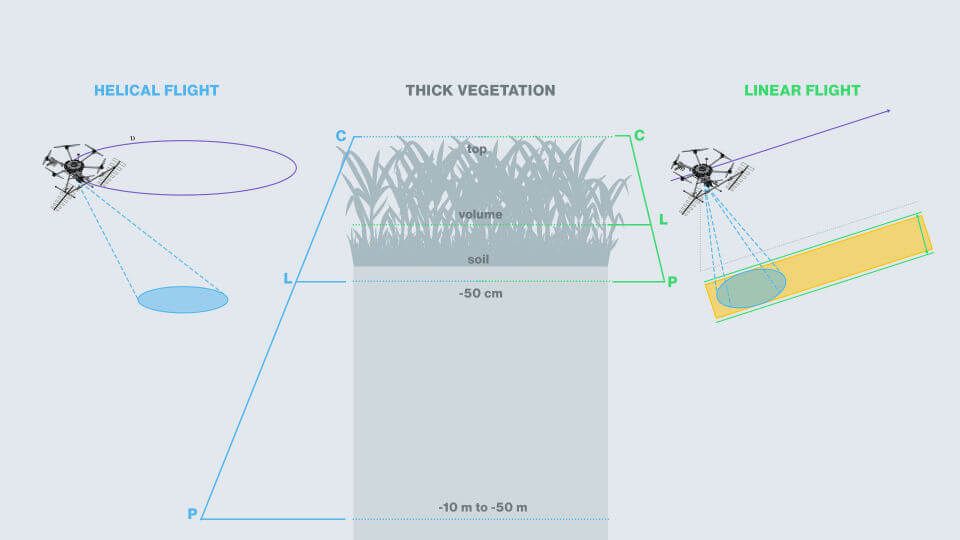
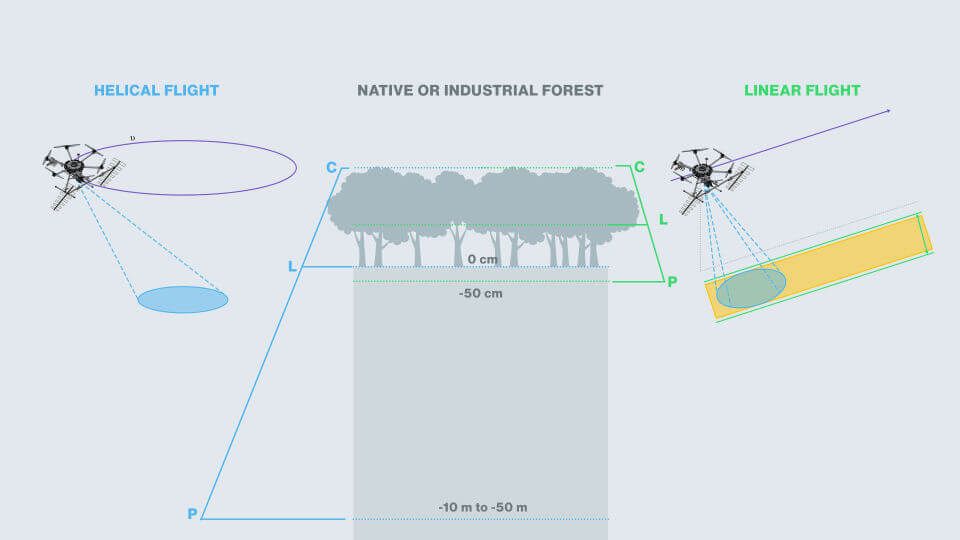
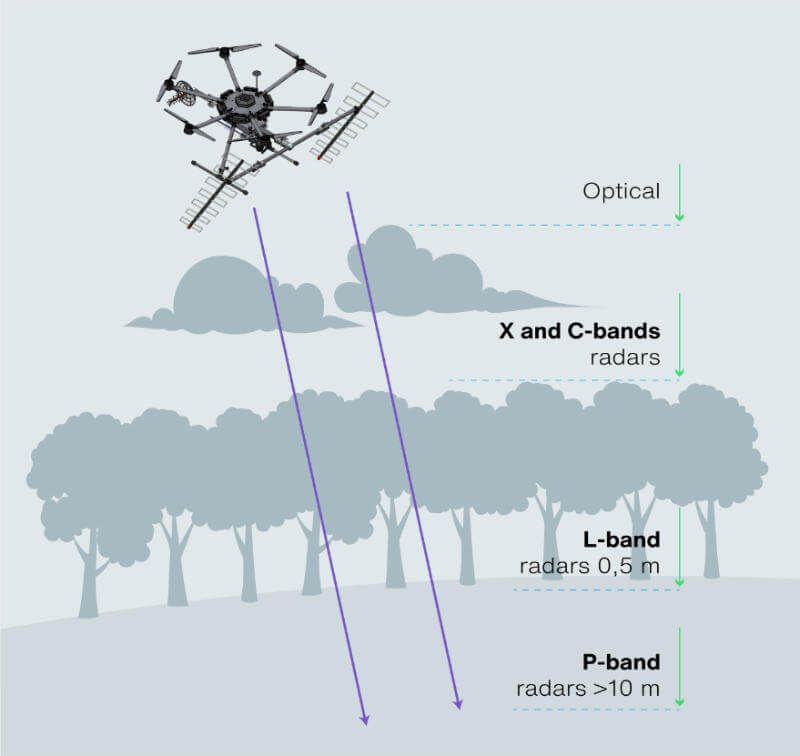
C-band antenna
Reaches the top layer of vegetation and soil.
L-band antenna
Mesures the volume of vegetation and top layer of subsoil.
P-band antenna
Penetrates the ground with or without forest.
Frequency
- P = 400 MHz
- L = 1,2 GHz
- C = 5,5 GHz
Wavelength
- P = 75 cm
- L = 25 cm
- C = 5,5 cm
Resolution up to
- 2 cm on C-band
- 6 cm on L-band
- 18 cm on P-band
Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) Flight Types
-
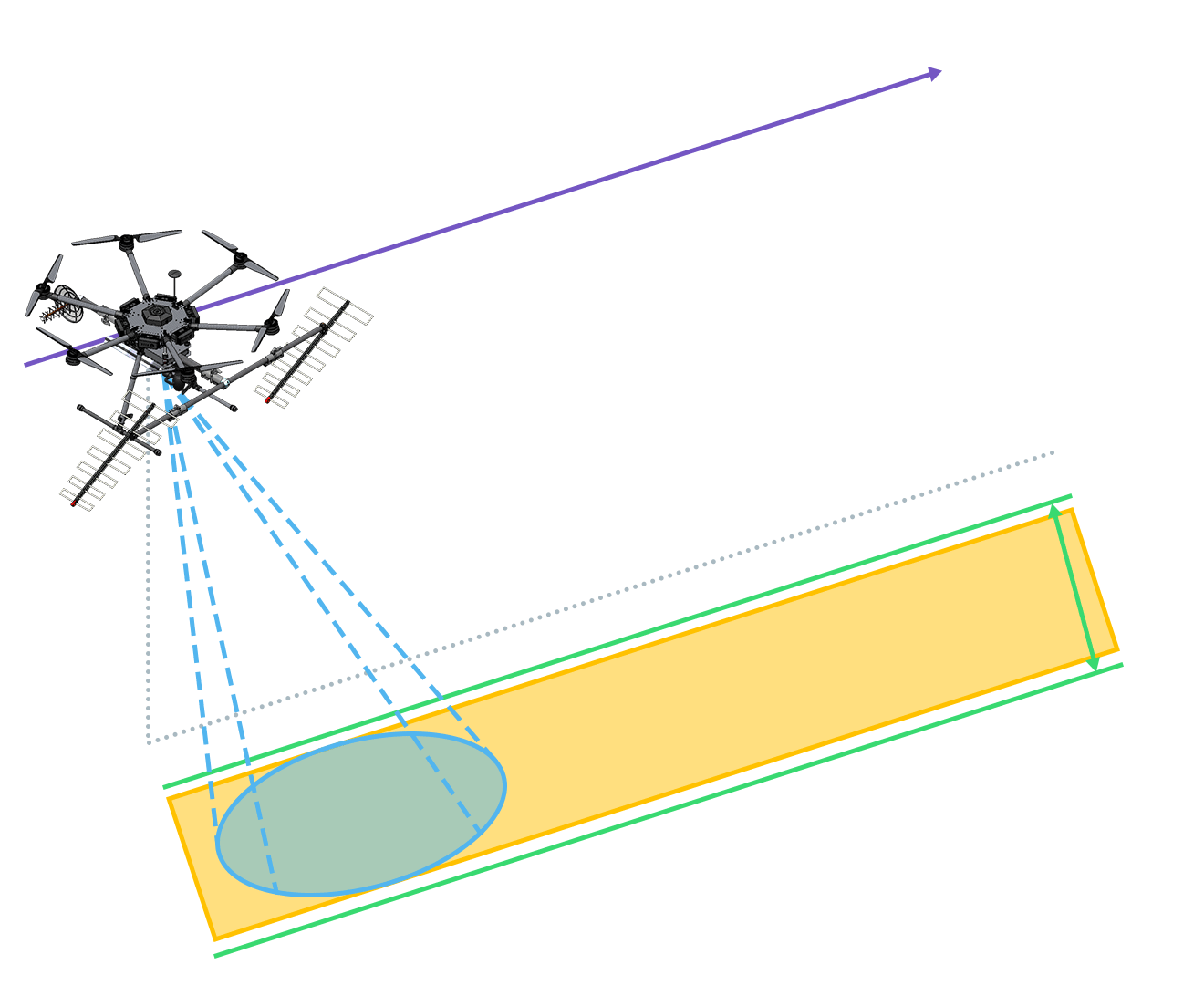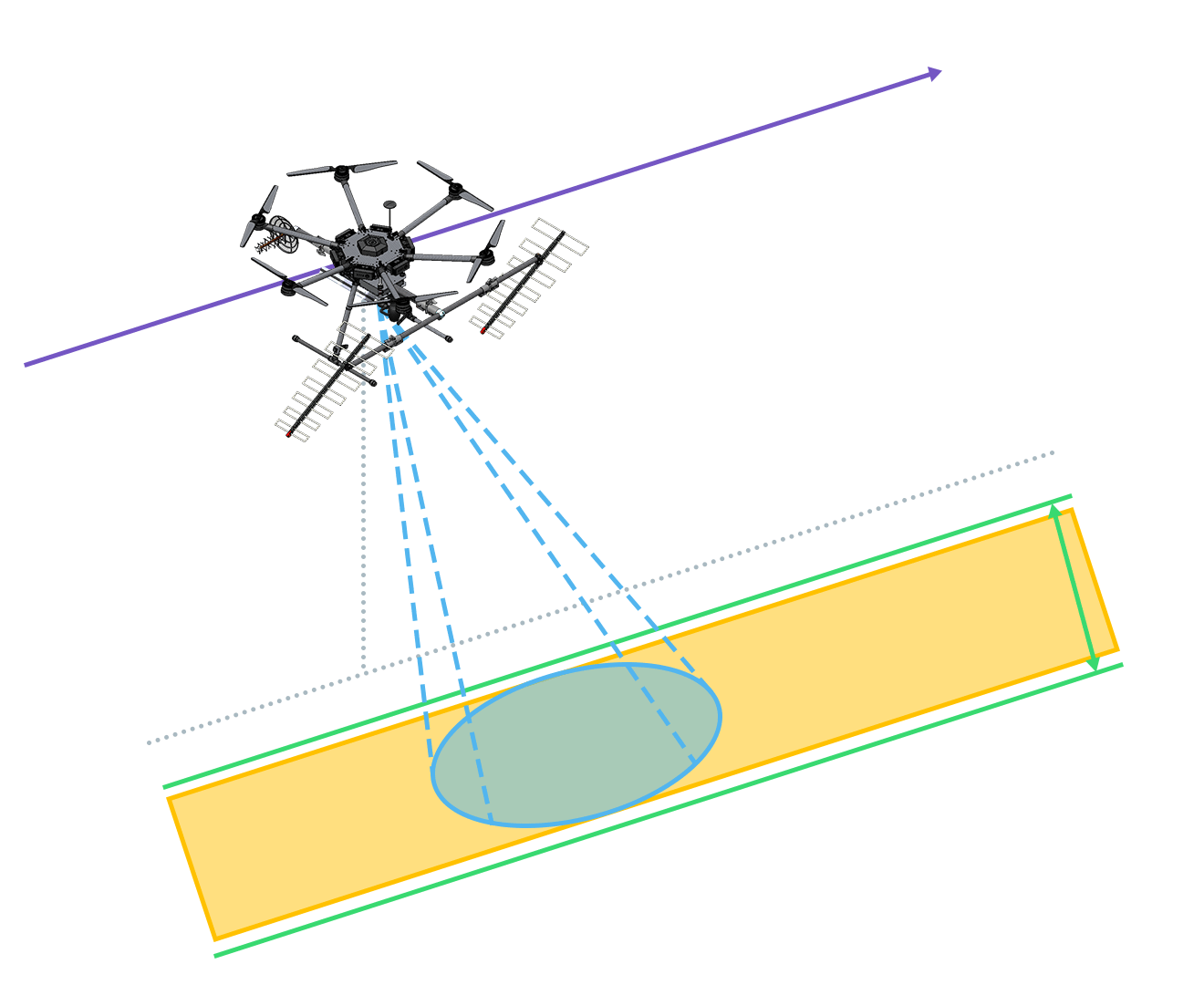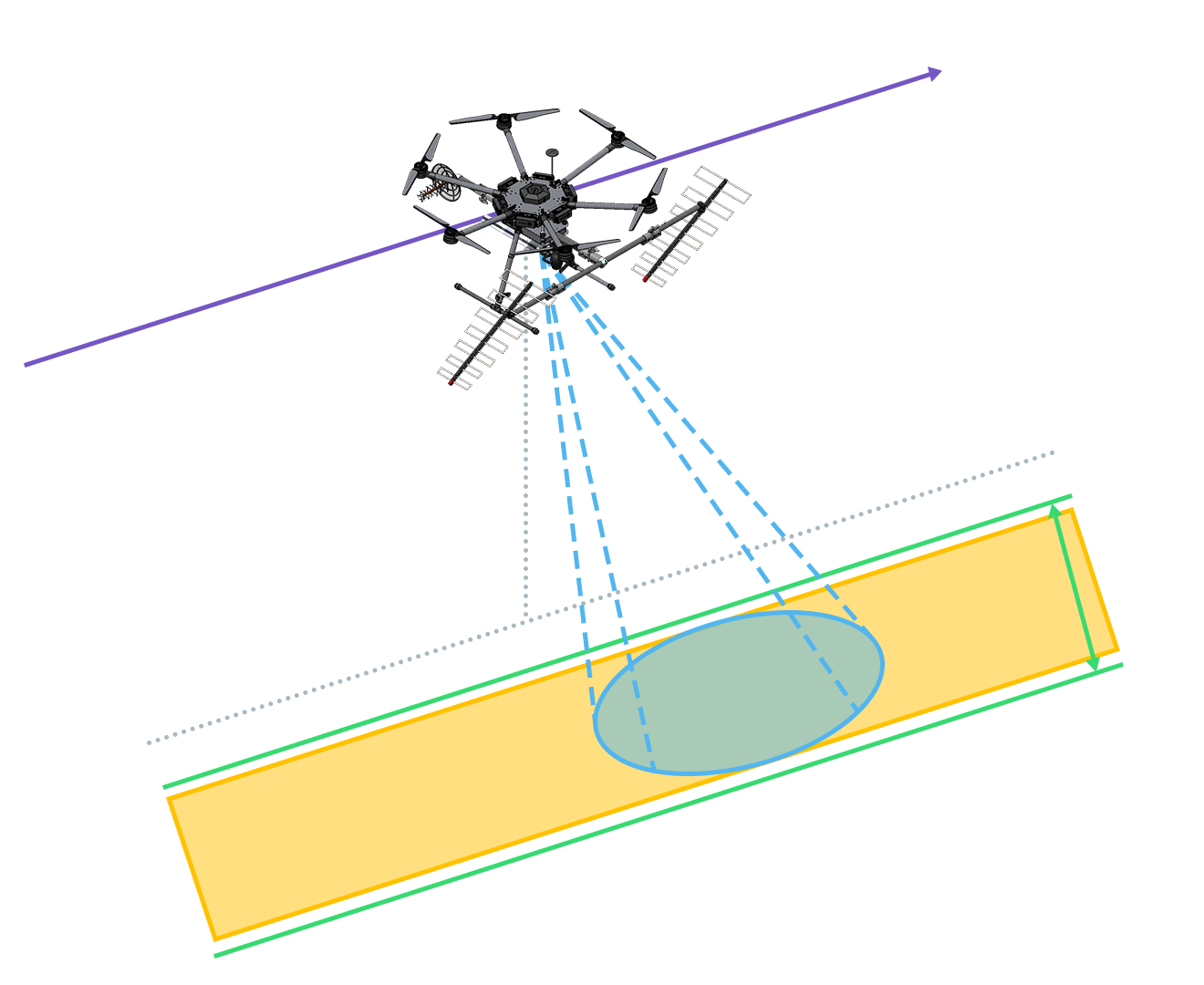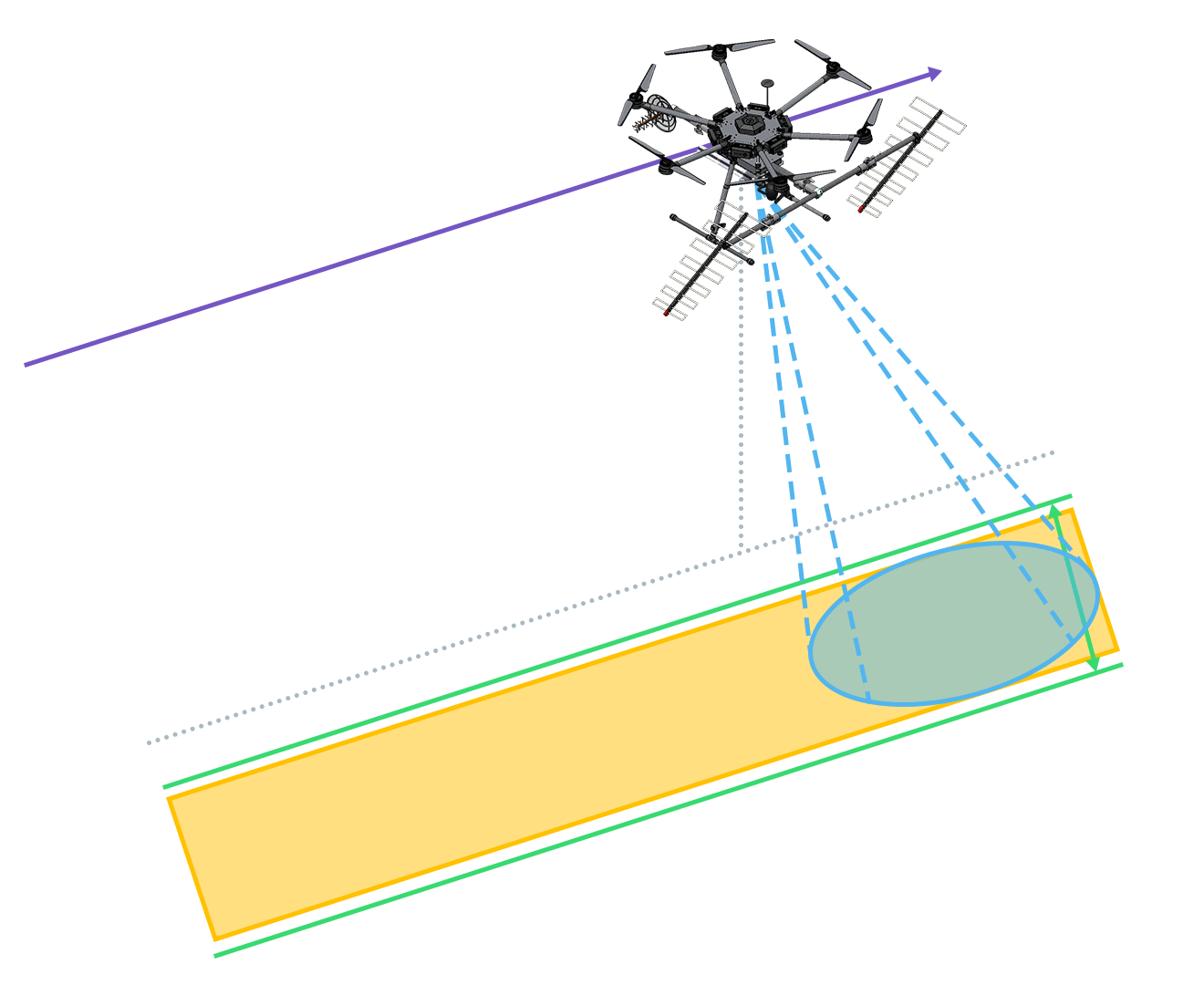
Linear Flight
Applies to topographic and wide area surveys, e.g. forest inventory, cartography or topography.
Larger coverage area, worse resolution. -
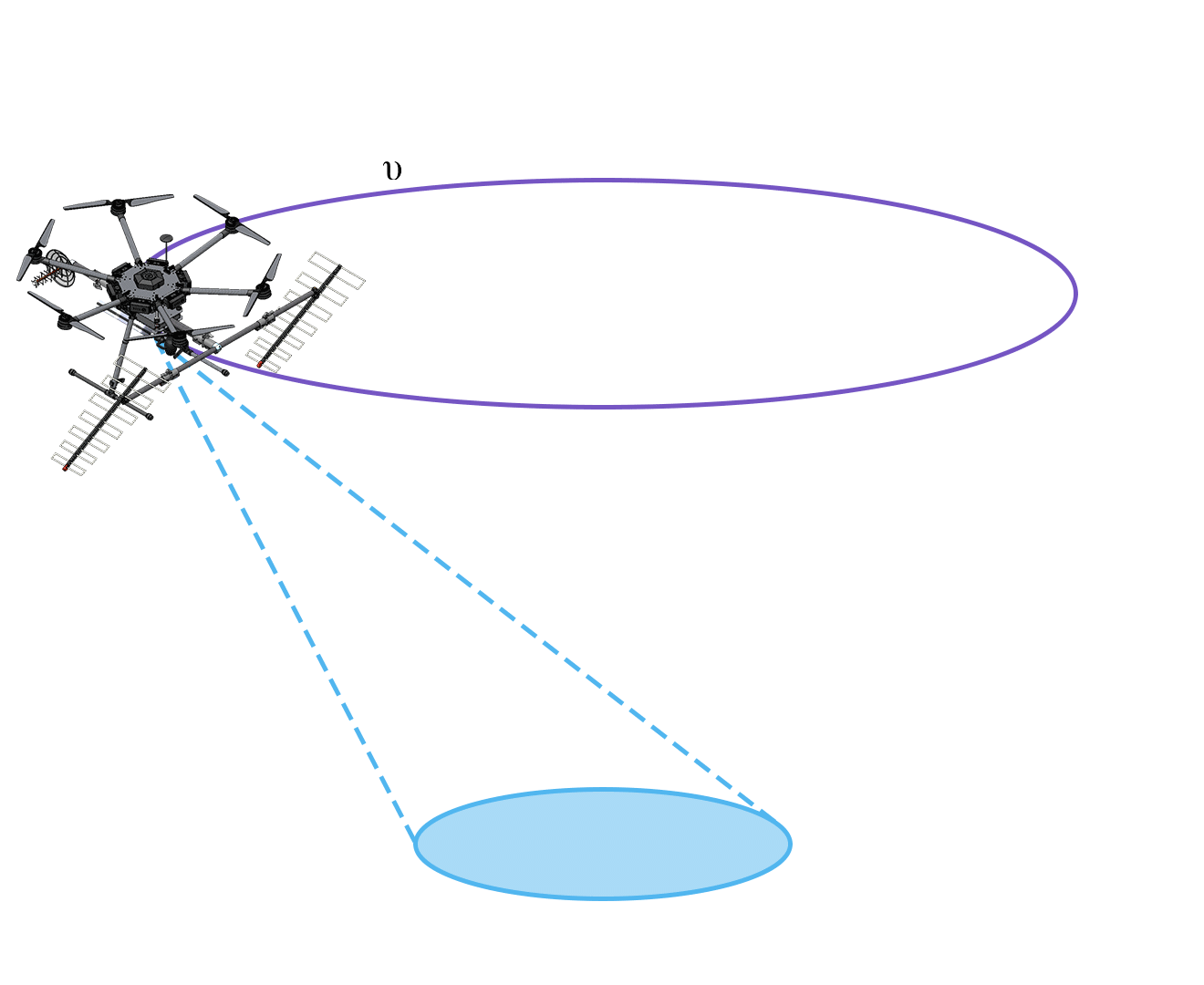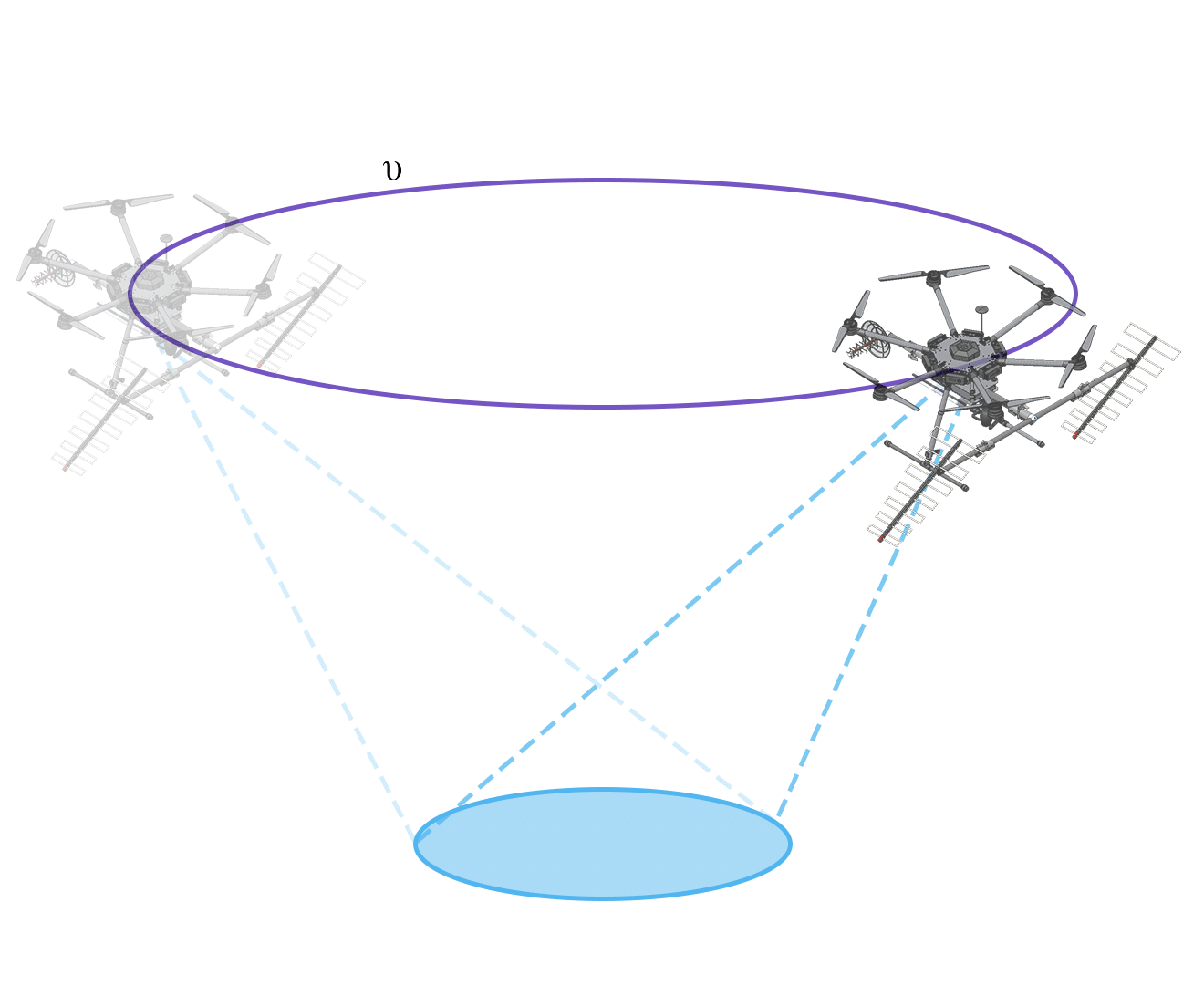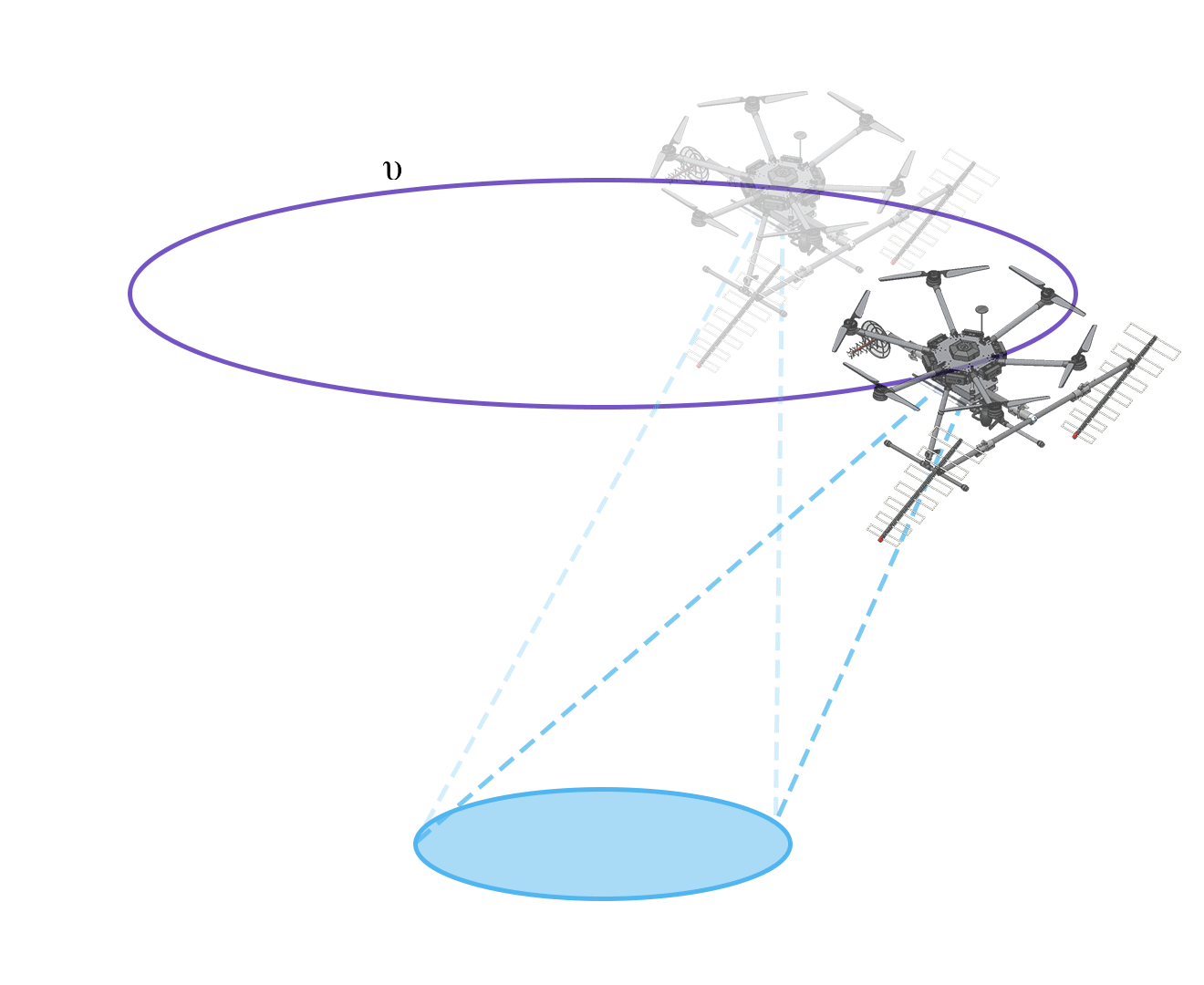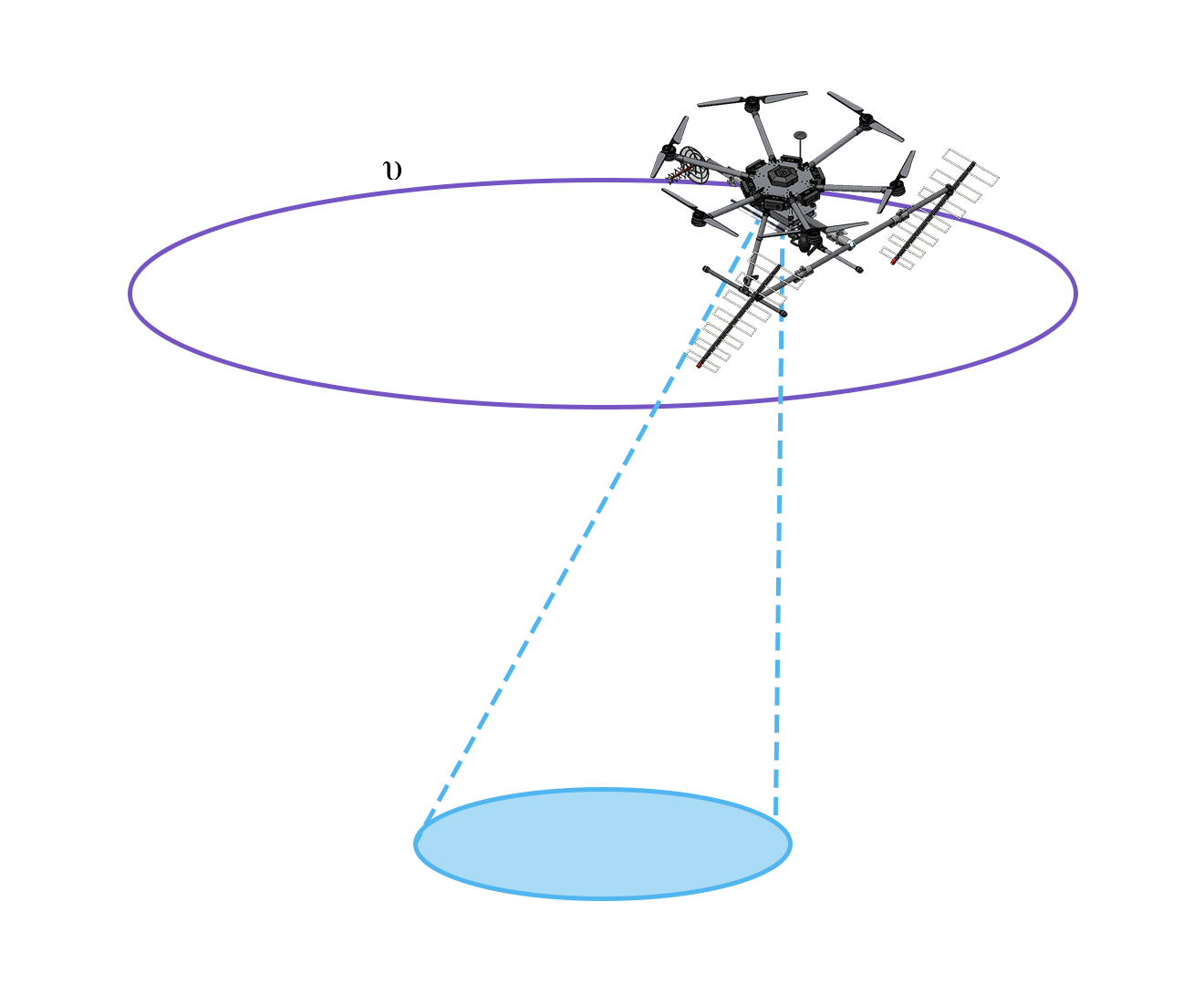
Helical Flight
Is for tomographic survey for applications requiring higher resolutions and penetration underground, example: location and sizing of anthills.
Smaller coverage area, better resolution.


Integration with drone
The drone is the means of transporting the radar to fly over the desired area. The only current restriction is that the drone needs to have a payload of 5 kilos, which would be the weight of the radar structure with the antennas.
We have already integrated the radar and antennas into different class 3 drones for our customers. We are constantly studying new equipment that has greater autonomy to increase productivity, since the radar has no time restriction for capturing information.
Differentials
Penetrates vegetation and soil
Operates independent of sunlight and cloud cover
Only three-band radar embedded in class 3 drone in the world
Automatic data processing
Technical Specifications
-
Coverage:
Up to 500 hectares/day in linear mode and up to 50 hectares/day i helical mode
-
Accuracy and detail:
Scales up to 1:5,000 and 1:500, respectively
-
Flight height:
120 meters
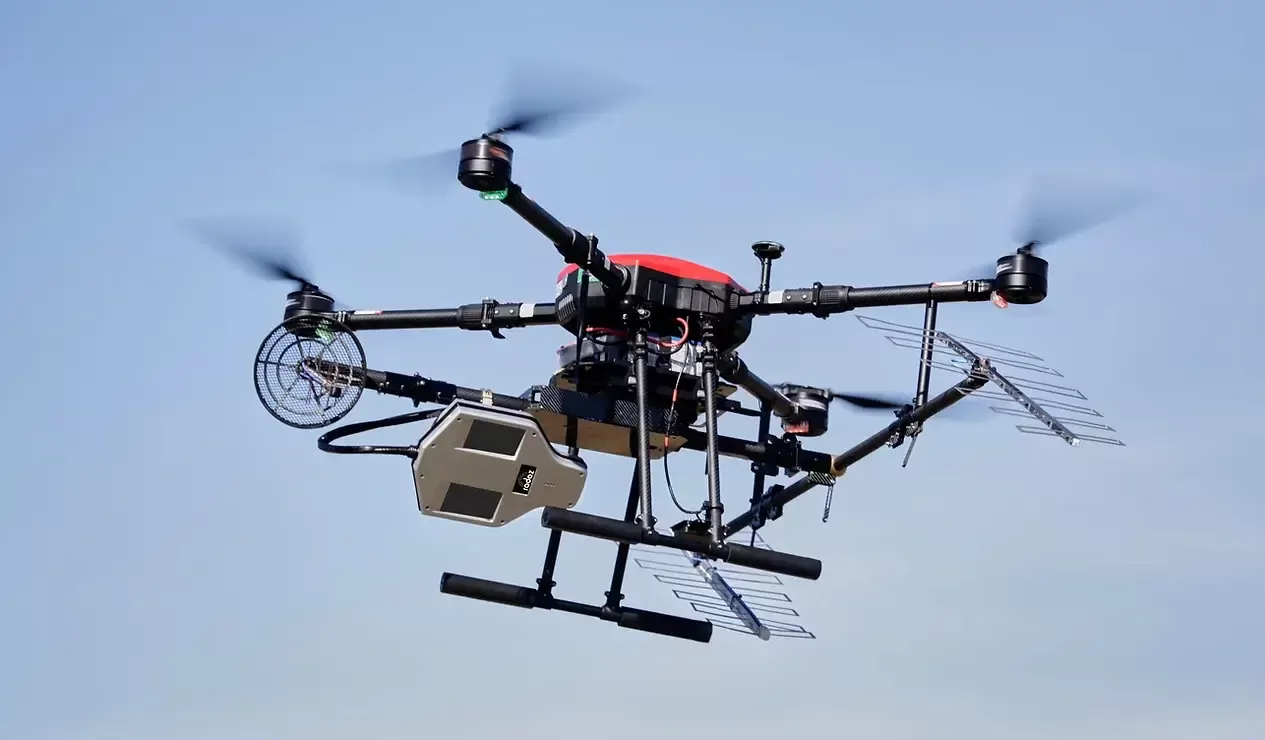


RD350
The RD350 system is equipped with 2 C antennas, 2 P antennas and 1 L antenna. In addition, there are two models of this product, both customized according to the market of operation:
KEEPER and EXPLORER


Keeper
Aimed at monitoring solutions, i.e., those that require revisits such as crop forecasting, plantation growth, soil moisture measurement, forest inventory, deforestation detection, measurement of soil subsidence and civil constructions, erosion and other recurring measures.


Explorer
Supports non-recurrent mapping and R&D demands. The non-recurring mappings are, for example, the accurate measurement of digital surface and terrain models and the acquisition of 1:500 scale images through circular and helical flights, becoming the reference base for revisit flights. The R&D flights are aimed at obtaining new products in the future, such as tomography for measuring subsurface subsidence, the detection of new types of anthills on the ground in industrial forests, the identification of pipes and galleries in the ground and 3D images for archaeology. The radar also has an interface to an external real-time processor.
Advantages of the RD350
Operates in C, L and P bands
The user can have their own radar operating simultaneously in P, L and C bands. It is the only three-band on-board Class 3 drone radar in the world, which offers cross-track interferometry in C and P bands simultaneously, along with polarimetric L-band.
Open data interface
Radar has an open interface to raw data and navigation data and comes with two open source back-projection processors: the traditional one and an FFBP.
Automatic data processing
Radar ground segment also processes the surveyed data automatically. The supplied laptop already has the entire processing library and delivers the data within the same acquisition time, i.e. if the flight lasts 25 minutes the images will be processed in 25 minutes.
The drone can perform revisits in up to 30 minutes, in addition to working with differential interferometry in the P, L and C bands, having a high precision inertial navigation system, which can survey up to 500 hectares per day in linear mode and 50 hectares per day in helical mode.
Available Products
The R&D Explorer RD350 is a research platform with open access to the acquired radar raw data and navigation data. Its precise inertial measurement unit and 2-frequency D-GNSS allow the accurate processing of linear, circular, helical or irregular flight patterns.
It is the most advanced tool for research in the field of SAR imagery, cross-track interferometry, differential interferometry, polarimetry, tomography and added-value products worldwide.
It is the unique P/L/C-band drone-borne SAR on the market with simultaneous acquisition of one-pass cross-track interferometry in both P and C bands and full polarimetric L-band. Moreover, an interface for an external onboard real-time processor is available.
The Forest Keeper RD350 is a turn-key drone-borne multi-band interferometric Synthetic Aperture Radar system for automated forest inventory. It automatically estimates the forest Volume, DBH or DAP, height, list of dominant tree heights and basal area with an accuracy of 2%.
The systems consists of:
1. Flight Segment
A radar cabinet with 2 C-band antennas, one L-band polarimetric antenna, two P-band antennas, GNSS antenna, light weight structure with mechanical interface and cable harness. The radar englobes a navigation system with an Inertial Measurement Unit and a 2-frequency GNSS receiver.
2. Ground Segment
A 2-frequency GNSS ground station, a tablet with the flight plan software for being attached to the drone remote control, a laptop with the processing software, a set of operation accessories and a lightweight transportation box. The transportation box has provision for the storage of all parts necessary for a standard survey.
3. A set of electronic manuals and check lists
The users may get the following
set of trainings

Trainings via videoconference
Explanation of the sub-systems, flight planning, assembly and disassembly of the flight and ground segments, flight survey, radar data processing and results interpretation will be presented. Also, the radar and navigation raw data format will be described allowing the processing by user’s software.

SAR Processing Tutorial
Starting with the format of the acquired radar raw data and navigation data. The User will also be aware of the SAR processing methodology, using an open-source back-projection SAR processor. The User will be trained to understand the radar raw data and navigation data format and to process them with an open-source processor. An open-source documentation about the algorithm is also available. The open-source processor can be upgraded by the user for attending its demands and applications.